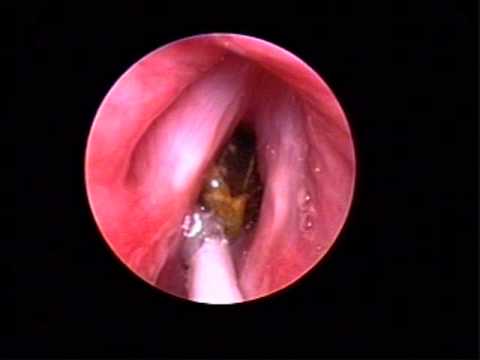
This video shows a sunflower seed causing near-complete airway obstruction. It is removed using an endoscopic instrument, resulting in a clear airway. Seeds and nuts are one of the most common foreign bodies to enter the airway.
Foreign body in throat
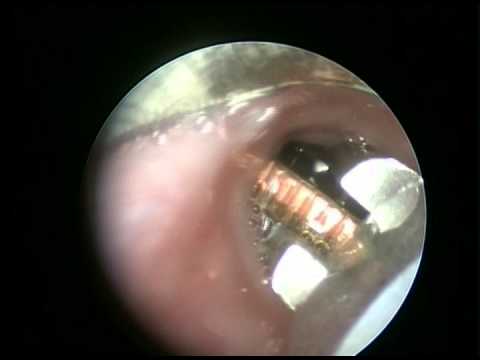
If you believe your child has a battery in their ear, nose or throat, THIS IS AN EMERGENCY. Your child must be evaluated by a healthcare professional immediately so that they can safely remove the battery.
Foreign bodies in the airway
A foreign body in the airway (choking) constitutes a medical emergency and requires immediate attention. The foreign body can get stuck in many different places within the airway. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, death by choking is a leading cause of death and injury among children younger than 4 years of age.
As with other foreign body problems, children tend to put things into their mouths when they are bored or curious. The child may then inhale deeply and the object may become lodged in the "airway" tube (trachea) instead of the "eating" tube (esophagus). Food may be the cause of obstruction in children who do not have a full set of teeth to chew completely, or those children who simply do not chew their food well. Children also do not have complete coordination of the mouth and tongue which may also lead to problems. Children under the age of four years are in the greatest danger of choking on small objects, including, but not limited to, the following:
|
|
Foreign bodies in the esophagus (swallowing tube)
This video shows a coin stuck in the esophagus. It is removed using an endoscopic grasping instrument. Coins are the most common foreign body in children that require removal from the esophagus.
Children need to be watched very closely to avoid a choking emergency. When food is swallowed it typically passes through the mouth to the throat and into the esophagus, which leads to the stomach. Sometimes a swallowed object is too large and gets stuck in the esophagus. The most common item that children swallow which gets stuck is a coin. Children under the age of four years are in the greatest danger of getting food or an object stuck in the esophagus.
What are the symptoms of a foreign body in the airway?
Foreign body ingestion requires immediate medical attention. The following are the most common symptoms that may indicate a child has inhaled a foreign body. Symptoms may include:
- Choking or gagging when the object is first inhaled
- Coughing
- Stridor
- Wheezing (a whistling sound, usually made when the child breathes out)
Although the initial symptoms listed above may subside, the foreign body may still be lodged in the airway. The following symptoms may indicate that the foreign body is still causing an airway obstruction:
- Stridor (a high-pitched sound heard when the child breathes)
- Wheezing
- Cough
- Pneumonia
- Voice changes
What are the symptoms of a foreign body in the esophagus?
A child with a foreign body in the esophagus may have any or all of the following symptoms:
- An initial choking episode
- Drooling
- Vomiting whenever trying to eat
- Inability to eat
Treatment for foreign bodies in the airway and esophagus
Treatment of the problem varies with the location of the foreign body. If the object is in the airway a laryngoscopy and bronchoscopy will need to be performed to remove the item. This procedure involves passing a rigid scope into the airway, viewing the airway to find the object and then using special forceps to remove the item. If the object is in the esophagus a scope is passed into the esophagus (esophagoscopy) and special tools are used to remove the stuck, swallowed item. Once the foreign body is removed the child typically recovers quickly.

Connect with us:
Download our App: