Salivary Gland Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection
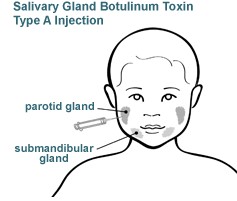
Botulinum toxin type A is a substance that causes reduced activity of muscles or glands. When injected into the salivary glands it can reduce saliva production. Botulinum toxin type A can also be injected into the submandibular gland (below the floor of the mouth) and the parotid gland (behind the jaw).
The substance is also known as Botox®.
Procedure
Using ultrasound for guidance, the physician will insert a small needle directly into the gland and inject a small amount of botulinum toxin type A. Sometimes a small bandage will be applied to the injection site. The procedure should take approximately 30 minutes.
Anesthesia
Patients receive either IV sedation or general anesthesia and are asleep for this procedure.
Pain
Your child may experience bruising, which is normal.
Risks
This is considered a low-risk procedure. Potential complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Temporary facial drooping (three to six months)
- Non-target site muscle injection, which can result in swallowing weakness
After Effects
You should see maximum effect within two to three weeks. The results will last three to six months.
Bathing
If a bandage is in place, you may remove it 24 hours after the procedure. Once the bandage is removed, your child may shower or take a bath.
Activity Restrictions
There are no activity restrictions after the procedure.
Connect with us:
Download our App: