Autosomal Recessive: Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia, Tay-Sachs Disease
You inherit genes from your biological parents in specific ways. One of the ways is called autosomal recessive inheritance.
What is autosomal recessive inheritance?
Autosomal recessive inheritance means that the gene in question is on one of the autosomes. These are numbered pairs of chromosomes, 1 through 22. Autosomes don't affect a child's sex.
"Recessive" means that two nonworking copies of the gene are needed to have the trait or disorder. One comes from the mother, and one from the father. If you have only one recessive gene, you are a "carrier" for the trait or disease. But you do not have any health problems from carrying one copy of the gene.
Most people don't know they carry a recessive gene for a disease until they have a child with the disease. Having another family member with the disease is also a way to know. All people carry about five or more recessive genes that cause genetic diseases or conditions. If you have a child with a recessive trait or disease, there is a 1 out of 4 chance that you will have another child with the same trait or disorder. This means that there is a 3 out of 4 chance that another child will not have the trait or disease.
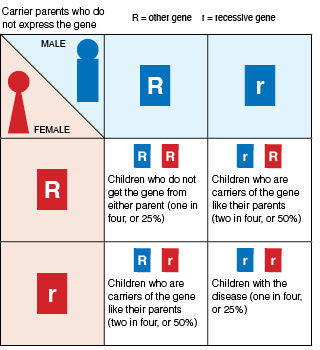
What are autosomal recessive disorders?
Changes in the DNA (mutations) have occurred over time in different parts of the world. Anyone can carry any type of recessive gene. But certain ethnic groups are more likely to carry certain recessive genes because of where the mutation started. For example, the gene that causes Tay-Sachs disease is commonly found in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. They are from Eastern Europe. This is where experts believe the mutation started. The disease also affects those who are not of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
What are some of the different types of autosomal recessive disorders?
Examples include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease.
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a common, inherited, single-gene disorder. It affects protein in the body. Anyone can have CF. But it is mainly found in white people. People with CF make very thick and sticky mucus that can lead to blockages and damage of body organs. The mucus interrupts the function of vital organs, especially the lungs. And it leads to chronic infections. CF also involves the pancreas and causes decreased absorption of essential nutrients. And it can cause damage to the reproductive system. Death most often occurs from respiratory failure. Other people with variants of CF may have only lung involvement, sinusitis, or infertility. CF has no cure. But better treatments are helping people live longer and healthier lives.
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is also a common, inherited, single-gene disorder. It's found mostly in African Americans. About 1 in 365 African-American babies is born with it. About 1 in 13 African Americans carries the gene for this disease. About 1 in 16,300 Hispanic American babies is also born with it.
Sickle cell disease (SCD) involves the hemoglobin in the red blood cells and their ability to carry oxygen. Normal red blood cells are smooth, round, and flexible, like the letter O. They can easily move through the vessels in our bodies. Sickle cells are stiff and sticky. When they lose their oxygen, they form into the shape of a sickle, or the letter C. Sickle cells tend to cluster together. They can't easily move through the blood vessels. The cluster causes a blockage. And it stops the movement of healthy oxygen-carrying blood. This blockage is what causes the problems of SCD.
Sickle cells live for about 15 days. Normal hemoglobin cells can live up to 120 days. The spleen can destroy sickle cells because of their shape and stiffness. The spleen helps filter the blood of infections. Sickle cells get "stuck" in this filter and die. Due to the lower number of hemoglobin cells moving in the body, a person with sickle cell has long-term (chronic) anemia. The spleen also suffers damage from the sickle cells, which block the healthy oxygen-carrying cells. After repeated blockages, the spleen is very small and does not work right. This raises the risk for infections. Infants and young children are at risk for life-threatening infections. Treatment includes emergency care for fevers and infections. It also includes vaccines, penicillin, and management of anemia. New gene therapies have been approved to treat SCD. Talk with your doctor (or your child's doctor) about these treatments.
Tay-Sachs disease
Tay-Sachs disease is a fatal disorder in children (usually by age 5). It causes a progressive degeneration of the central nervous system. It is caused by the absence of an enzyme called hexosaminidase A (or hex A). Without hex A, a fatty substance builds up on the nerve cells in the body, particularly the brain. The process begins early in pregnancy when the baby is developing. It is not apparent until several months after the birth. To date, there is no cure for Tay-Sachs. About 1 in 27 people of European Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry carries the Tay-Sachs gene.
Connect with us:
Download our App: