Call us today
Contact us to learn more about our Motion Analysis Laboratory or to schedule an appointment.
An upper limb analysis looks at the motion of the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand. The test has several components, together they provide a comprehensive picture of the various factors contributing to the upper limb disorder.
Video – The patient is videotaped while performing a variety of upper limb motions, including:
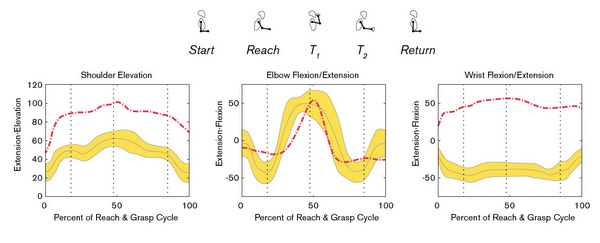
Kinematics – Kinematics provides a 3-D picture of how the upper limb moves during a functional reach and grasp task. Reflective balls are taped onto the arms, trunk (shoulders to hips) and pelvis. Digital cameras record the balls’ movements to measure joint motion at the trunk, shoulder, elbow and wrist.
Electromyography (EMG) – Dynamic EMG can help determine which upper limb muscles act correctly during functional tasks. These tasks may include:
Muscles tested during an EMG include those targeted for tendon transfer or neuromuscular blockade, such as flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor carpi radialis or brachioradialis. Prior to surgery, EMG is used to identify phasic, continuously active, or out-of-phase muscle activity to guide surgery and other medical treatment. Phasic muscles are active at the appropriate times. Out-of-phase muscles are active when they should be inactive. A typical upper limb analysis lasts approximately 2 hours.
After the upper limb analysis is completed, you and your health care provider will receive a:
Connect with us:
Download our App: