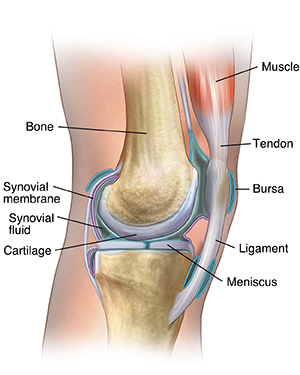
Anatomy of a Joint
Joints are the areas where 2 or more bones meet. Most joints are mobile, allowing the bones to move. Joints consist of the following:
Cartilage. This is a type of tissue that covers the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce the friction of movement within a joint.
Synovial membrane. A tissue called the synovial membrane lines the joint and seals it into a joint capsule. The synovial membrane secretes a clear, sticky fluid (synovial fluid) around the joint to lubricate it.
Ligaments. Strong ligaments (tough, elastic bands of connective tissue) surround the joint to give support and limit the joint's movement. Ligaments connect bones together.
Tendons. Tendons (another type of tough connective tissue) on each side of a joint attach to muscles that control movement of the joint. Tendons connect muscles to bones.
Bursas. Fluid-filled sacs, called bursas, between bones, ligaments, or other nearby structures. They help cushion the friction in a joint.
Synovial fluid. A clear, thick fluid secreted by the synovial membrane.
Meniscus. This is a curved part of cartilage in the knees and other joints.
What are the different types of joints?
There are many types of joints, including joints that don’t move in adults, such as the suture joints in the skull. Joints that don’t move are called fixed. Other joints may move a little, such as the vertebrae. Examples of mobile joints include the following:
Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.
Hinge joints. Hinge joints, such as in the fingers, knees, elbows, and toes, allow only bending and straightening movements.
Pivot joints. Pivot joints, such as the neck joints, allow limited rotating movements.
Ellipsoidal joints. Ellipsoidal joints, such as the wrist joint, allow all types of movement except pivotal movements.
Connect with us:
Download our App: