Overview of the Male Anatomy
This is an overview of the male reproductive anatomy:
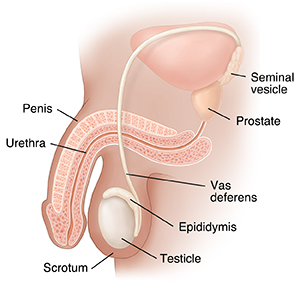
Scrotum. The bag of skin that holds and helps to protect the testicles. The testicles make sperm. To do this, the temperature of the testicles needs to be cooler than the inside of the body. This is why the scrotum is located outside of the body.
Testes (testicles). The testes are 2 small organs that are found inside the scrotum. The testes make sperm. They also help make a hormone called testosterone. Testosterone is an important hormone during male development and maturation. It plays a key role in developing muscles, deepening the voice, and growing body hair.
Epididymis. A long tube that is located near each testicle. The epididymis is the tube the moves the sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens.
Vas deferens. The tube where the sperm is stored. It also carries the sperm out of the scrotal sac. The vas deferens is between the epididymis and the urethra. It connects them together.
Seminal vesicles. The sac-like glands that lie behind the bladder and release a fluid that forms part of the semen.
Prostate gland. This gland is about the size of a walnut. It surrounds the neck of the bladder and the tube that carries urine from the bladder (the urethra). The prostate gland secretes a slightly alkaline fluid that forms part of the seminal fluid, a fluid that carries sperm.
Urethra. This is a tube that allows urine to flow outside the body. It's also the channel for semen to pass during ejaculation. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten. This squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals happen in the correct order, normal urination happens.
Penis. This is the external reproductive organ. The penis is made up of 2 parts, the shaft and the glans. The glans is the tip of the penis. The shaft is the main part of the penis. It contains the tube (urethra) that drains the bladder. A penis has a foreskin. This is a skin covering over the tip of the penis. Some people are circumcised when they are babies. This means that the foreskin is removed.
Connect with us:
Download our App: