Torn Meniscus
What is a torn meniscus?
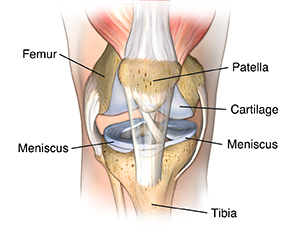
There are three bones in the knee. These are the femur, tibia, and patella. The ends of those bones are covered with cartilage. This is a smooth material that cushions the bone and allows the joint to move easily without pain. The cartilage acts as a shock absorber. Between the bones of the knees are two crescent-shaped disks of connective tissue, called menisci. These also act as shock absorbers to cushion the lower part of the leg from the weight of the rest of the body.
What causes a torn meniscus?
Meniscus tears can happen during a sudden rotating movement while bearing weight, such as when twisting the upper leg while the foot stays in one place during sports and other activities. This is known as a traumatic tear. Or meniscal tears can develop over time (degenerative). This is when routine activities, such as jogging or yard work, cause tears in the meniscus that have been weakened over time because of age, arthritis, or other conditions. Degenerative meniscal tears are most common in adults older than 40. Tears can be minor, with the meniscus staying connected to the knee. Or they can be major, with the meniscus barely attached to the knee by a cartilage thread.
What are the symptoms of a torn meniscus?
Each person may have different symptoms. But the most common symptoms are:
Pain, especially when holding the knee straight
Swelling and stiffness
Knee may catch, click, or lock
Knee may feel weak or unstable
Less range of motion
These symptoms may look like other health conditions or problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is a torn meniscus diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam. You may also need:
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
MRI. This test uses a combination of large magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. It can often find damage or disease in a surrounding ligament, tendon, bone, or muscle.
Arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used for conditions of a joint. It uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope). The tube is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen. They are used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint. The procedure also may find bone diseases and tumors, as well as determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
How is a torn meniscus treated?
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how bad the condition is.
Treatment may include:
Resting, icing, and elevating your knee
Compression bandage
Medicine to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, such as ibuprofen
Muscle-strengthening exercises
Physical therapy
Arthroscopic surgery
What are possible complications of a torn meniscus?
An untreated torn meniscus can result in instability of the knee and lasting pain. It can also increase your risk of osteoarthritis.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if your knee:
Locks or catches or makes a clicking, popping, or grinding sound
Is painful and swollen
Feels weak or buckles
Key points about a torn meniscus
Torn meniscus is often caused by a twisting movement of the knee while bearing weight. Or it can develop over time from routine activities.
A torn meniscus causes pain, locking, or clicking, and weakness of the knee.
Exercises, medicine, and arthroscopy may be used to treat a torn meniscus.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are and when they should be reported.
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
Know how you can contact your healthcare provider if you have questions, especially after office hours or on weekends and holidays.
Connect with us:
Download our App: